Energy-efficient windows are a smart investment for any homeowner. They not only save you money on heating and cooling bills but also have a positive environmental impact. This guide explores the different types, benefits, and technologies behind these windows, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions.
From double-pane to triple-pane options, and low-E coatings, there’s a window designed to meet your needs. We’ll delve into the key features, installation, and maintenance to ensure you get the most out of your investment.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows

Source: windows.net
Energy-efficient windows are more than just a trendy upgrade; they offer a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond aesthetics. These windows, designed with advanced technologies and materials, dramatically impact your home’s energy consumption, resulting in significant financial savings and a positive environmental footprint.Beyond cost savings, energy-efficient windows enhance indoor comfort and contribute to a healthier living environment. They help regulate temperature fluctuations, minimizing drafts and improving overall comfort levels.
Financial Advantages of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows represent a sound investment with substantial long-term financial returns. They reduce heating and cooling costs, lowering your utility bills over time. These savings can quickly offset the initial investment, making energy-efficient windows a worthwhile addition to any home.
- Reduced Utility Bills: Energy-efficient windows dramatically decrease the amount of energy needed to heat and cool your home. This translates directly to lower utility bills, saving you money each month. For instance, homes with properly installed energy-efficient windows often experience a 10-20% reduction in energy bills compared to homes with standard windows.
- Increased Home Value: Energy-efficient windows enhance the overall appeal and value of your home. Potential buyers often recognize the financial benefits of these upgrades, leading to a higher resale value for your property. A home with energy-efficient features is often more attractive to buyers, potentially increasing its value by several thousand dollars.
- Potential for Tax Credits and Rebates: Many governments offer tax credits and rebates for energy-efficient home improvements, such as installing energy-efficient windows. These incentives can further reduce the overall cost of the upgrade, making it even more appealing.
Environmental Impact of Energy-Efficient Windows
Choosing energy-efficient windows has a positive impact on the environment. By reducing energy consumption, you lessen the demand for fossil fuels, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. This contributes to a healthier planet for future generations.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By decreasing the amount of energy needed to heat and cool a home, energy-efficient windows lower the reliance on fossil fuels, directly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This smaller carbon footprint contributes to a more sustainable environment.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Energy-efficient windows reduce the need for energy production, which in turn conserves valuable natural resources. Lower energy demand means less reliance on the extraction and processing of raw materials, promoting sustainability.
- Reduced Air Pollution: Lowering energy consumption through energy-efficient windows results in reduced emissions of air pollutants, improving air quality and reducing negative health impacts.
Comfort and Health Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows significantly improve indoor comfort and promote better health. They help maintain a stable indoor temperature, minimizing drafts and temperature fluctuations, leading to a more comfortable living environment.
- Enhanced Indoor Comfort: Energy-efficient windows help maintain a consistent indoor temperature, reducing drafts and fluctuations, creating a more comfortable living environment. This steady temperature reduces the need to constantly adjust the thermostat, leading to better comfort.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: By minimizing drafts and temperature fluctuations, energy-efficient windows reduce the movement of dust and allergens, leading to improved indoor air quality. This positive impact on air quality is beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
- Reduced Noise Pollution: Energy-efficient windows often incorporate features that reduce noise transmission. This results in a quieter home environment, promoting better sleep and overall well-being.
Reduction in Heating and Cooling Costs
Energy-efficient windows directly contribute to lowering heating and cooling expenses. By reducing energy loss, they maintain a stable indoor temperature, minimizing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
- Minimized Energy Loss: Energy-efficient windows are designed to minimize energy loss through thermal insulation. This reduces the amount of energy required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, leading to lower heating and cooling bills.
- Consistent Indoor Temperature: By regulating temperature fluctuations, energy-efficient windows maintain a consistent indoor environment, eliminating the need for frequent adjustments to the thermostat. This consistent temperature minimizes energy waste and reduces overall costs.
- Long-term Savings: The reduced energy consumption over time translates to significant long-term savings on heating and cooling bills. These savings can quickly pay for the initial investment in energy-efficient windows.
Long-Term Savings Associated with Energy-Efficient Windows
The long-term savings from energy-efficient windows are substantial. The initial investment is often recovered within a few years through reduced utility bills, and the benefits continue throughout the lifespan of the windows.
- Payback Period: The payback period for energy-efficient windows is often shorter than expected, with many homeowners seeing a return on investment within a few years due to lower energy bills. For example, a homeowner in a cold climate may see a payback period of 3-5 years, while a homeowner in a moderate climate might see a payback of 5-7 years.
- Lifetime Savings: The long-term savings from energy-efficient windows continue throughout the lifespan of the windows, providing consistent cost reductions over the years. These savings add up significantly over time.
Key Features and Technologies
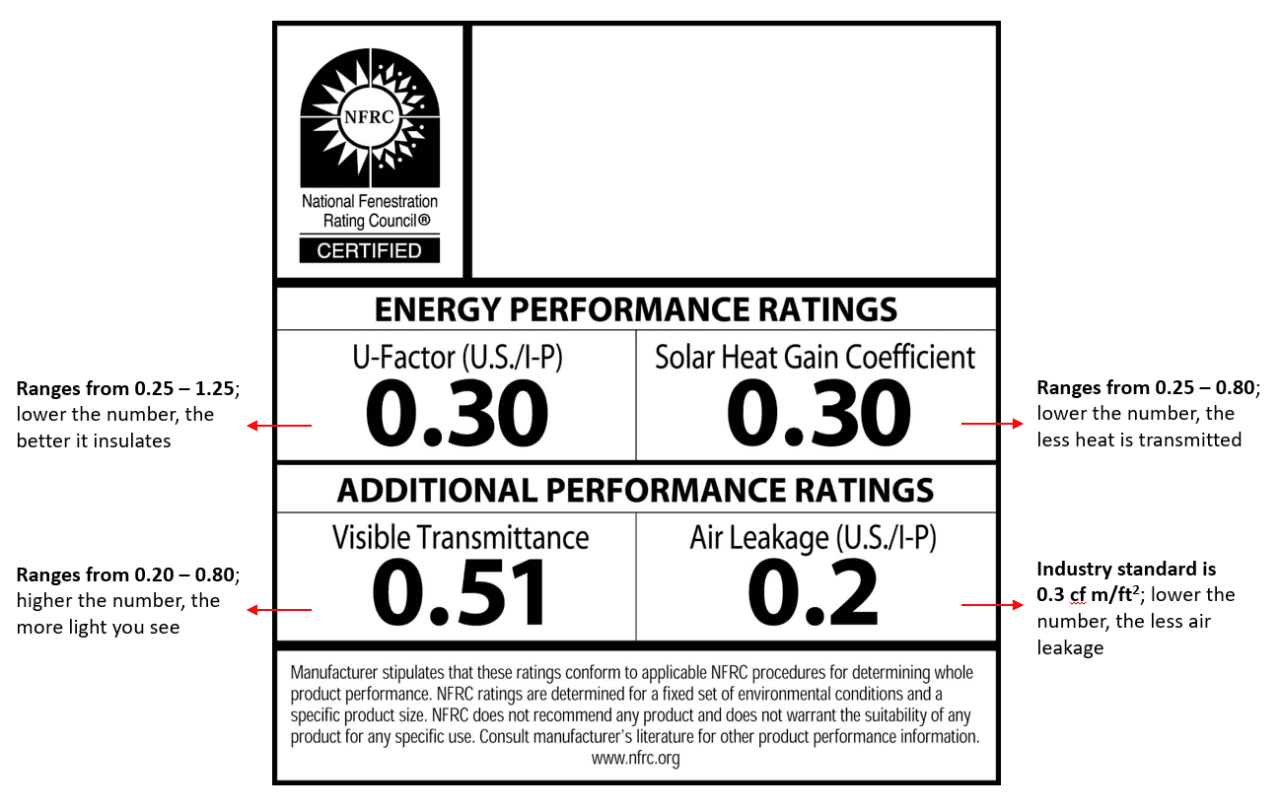
Source: championwindow.com
Energy-efficient windows go beyond just looking good; they play a crucial role in reducing your energy bills and promoting sustainability. Understanding the key technologies behind these windows is essential to making informed choices. This section delves into the specific features and technologies that contribute to their energy-saving capabilities.
Low-E Coatings
Low-E, or low-emissivity, coatings are a crucial component of energy-efficient windows. These microscopic layers, typically metallic oxides, are applied to the glass surface. They selectively control the passage of infrared radiation. By reflecting heat back towards its source, these coatings minimize unwanted heat transfer, whether it’s heat entering in the summer or escaping in the winter. This significantly reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling, leading to lower energy consumption.
Window Frame Materials
Window frames significantly impact the overall energy performance of a window. The material used for the frame directly influences its insulating properties. Consideration should be given to materials with high thermal resistance. For example, thermally broken frames, often using multiple layers of insulation, limit heat transfer through the frame. This minimizes the heat loss or gain through the frame itself, complementing the insulating properties of the glass.
Wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiberglass are common frame materials, each with varying thermal characteristics. Proper installation and sealing around the frame perimeter are also crucial for maximizing energy efficiency.
Gas Fills
The space between the panes of glass in a double- or triple-pane window is often filled with inert gases like argon or krypton. These gases are significantly less conductive than air. This reduced conductivity significantly enhances the insulating properties of the window. The lower thermal conductivity of these gases minimizes heat transfer between the panes, reducing heat loss or gain.
Argon is a common choice due to its cost-effectiveness, while krypton, with its even lower conductivity, offers enhanced insulation for a higher cost.
Design Considerations for Energy-Efficient Window Frames
Designing energy-efficient window frames involves more than just selecting materials. Proper sealing is crucial. The gaps between the frame and the glass must be tightly sealed to prevent air infiltration. This minimizes heat transfer, and airtight seals help reduce drafts. Thermal breaks are another important design consideration, creating a barrier to heat transfer through the frame itself.
These features, along with careful consideration of the specific climate, contribute to the overall energy efficiency of the window.
Summary Table of Key Technologies
| Technology | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low-E coatings | Reduces heat transfer by reflecting infrared radiation. | Reduces heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. |
| Gas fills (e.g., argon, krypton) | Significantly improves insulation by reducing thermal conductivity. | Argon is a common and cost-effective choice; krypton offers superior insulation. |
| Frame materials (e.g., thermally broken frames) | Minimizes heat transfer through the frame. | Reduces heat loss/gain through the frame structure. |
Installation and Maintenance
Installing energy-efficient windows requires careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper installation minimizes drafts, maximizes energy savings, and avoids costly repairs down the line. Maintenance procedures, when followed regularly, will help keep your windows operating efficiently and looking their best for years to come.
Energy-efficient windows are a great way to save money on your energy bills. Modern designs often incorporate minimalist glass design elements, like Minimalist glass design techniques, which can improve both aesthetics and efficiency. These sleek, streamlined designs contribute to the overall energy-saving performance of the windows.
Installation Steps
Installing energy-efficient windows involves several crucial steps. First, ensure the existing window frame is sound and properly prepared. Then, carefully measure and cut the new window frames to fit the opening. Next, install the window frame and secure it to the opening using appropriate fasteners. After this, the new window is installed and sealed, ensuring proper weatherproofing and insulation.
Finally, check all seals and hardware to guarantee proper operation and energy efficiency.
Tools and Materials
A range of tools and materials are essential for a successful installation. Commonly used tools include measuring tapes, saws, drills, and screwdrivers. Specific materials needed depend on the type of window and the construction of the house, but often include window frames, glass panes, weatherstripping, caulk, and fasteners. Always use the right tools and materials appropriate for the type of window frame and the structure of the building to ensure a secure and efficient installation.
Sealing and Weatherstripping
Proper sealing and weatherstripping are critical to achieving the energy-saving potential of energy-efficient windows. Improper sealing can lead to drafts, significant energy loss, and discomfort. High-quality weatherstripping around the window frame prevents air leaks, and proper caulking fills any gaps or cracks. These elements create a tight seal, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving the performance and longevity of energy-efficient windows. Clean the window frames and glass regularly with mild soap and water to remove dirt and grime. Inspect the weatherstripping and seals for any signs of damage or wear and tear. If any damage is found, promptly address it to maintain the seal. This ensures the window’s efficiency and appearance.
Lubricate moving parts, such as hinges and rollers, periodically to maintain smooth operation.
Common Installation Issues
Several issues can arise during the installation of energy-efficient windows. Incorrect measurements can lead to misalignment or improper fit. Using the wrong fasteners can cause structural problems or damage the window frame. Improper sealing can result in air leaks and reduced energy efficiency. Carefully reviewing the manufacturer’s instructions and consulting with a professional installer can help avoid these problems.
Problems can also arise if the window frames are not properly prepared, if the materials are not appropriate for the job, or if the installation steps are not followed correctly.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world applications demonstrate the significant energy savings and cost-effectiveness of energy-efficient windows. These case studies offer valuable insights into the practical implementation and impact of such windows in diverse settings. From residential homes to commercial buildings, the benefits are evident.Analyzing successful installations reveals key factors that contribute to the overall effectiveness of energy-efficient windows. These factors, ranging from window type and material to installation techniques and climate considerations, will be explored in detail.
The cost-effectiveness of energy-efficient windows is further highlighted through the examination of different case studies.
Real-World Examples of Successful Installations
Numerous projects showcase the positive impact of energy-efficient windows. One notable example is a series of renovations in a multi-family housing complex in a cold climate. By replacing traditional windows with triple-pane, low-e windows, residents experienced substantial reductions in heating costs. Similarly, a retail store in a hot and humid climate saw cooling costs decrease significantly after installing windows with specialized coatings and improved insulation.
Impact on Energy Consumption
Quantifiable data underscores the impact of energy-efficient windows. In the multi-family housing example, energy consumption for heating decreased by an average of 25% after the window upgrades. This translates to significant cost savings for the residents. Similar reductions in energy consumption for cooling were observed in the retail store case study.
Design and Implementation Details of Different Case Studies
Different case studies employed various strategies for window design and installation. The multi-family housing complex utilized triple-pane windows with argon gas fills and low-e coatings for enhanced insulation. The retail store employed advanced window coatings, like low-e coatings, that effectively reduced heat gain in the summer. The installation process adhered to building codes and industry best practices to ensure optimal performance.
Cost-Effectiveness in Different Climates
The cost-effectiveness of energy-efficient windows varies depending on the climate. In colder climates, the payback period for energy-efficient windows is typically shorter due to substantial savings in heating costs. In warmer climates, the payback period may be longer, but the reduction in cooling costs can still yield a positive return on investment over time. The initial investment in energy-efficient windows may be higher, but the long-term savings in energy consumption can often outweigh the initial cost.
Energy-Efficient Window Needs for Different Homes
The specific energy-efficient window needs vary based on the type of home and its characteristics. Single-family homes, for example, often require windows that optimize for both heating and cooling needs, depending on the climate zone. Multi-family buildings may require larger window areas and windows with higher thermal performance to meet the collective needs of multiple units. Commercial buildings might require different considerations depending on their specific function and usage patterns.
| Home Type | Energy-Efficient Window Needs |
|---|---|
| Single-Family Homes | Optimize for heating and cooling needs based on climate zone |
| Multi-Family Buildings | Larger window areas with high thermal performance |
| Commercial Buildings | Specific considerations depending on function and usage |
Future Trends in Energy-Efficient Windows
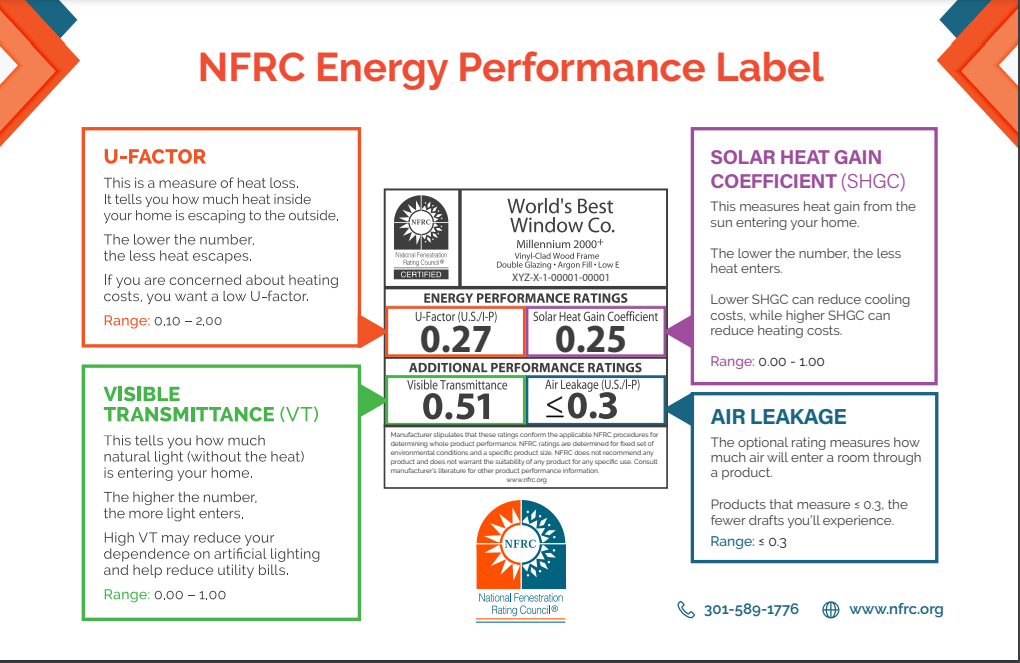
Source: efficientwindows.org
The energy efficiency of windows is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the need for sustainable solutions. New materials and designs are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, promising significant reductions in energy consumption and improved comfort levels. This evolution is directly tied to the growing global focus on climate change mitigation.
Emerging Technologies in Window Design
Innovations in window design are focused on enhancing insulation and light control. This includes the integration of advanced coatings and materials, along with sophisticated manufacturing techniques. The use of advanced materials like low-emissivity (low-e) coatings, which reflect heat, and laminated glass, which reduces sound transmission, are already common, and future developments will further refine these approaches. Smart windows, incorporating electrochromic or thermochromic technologies, are also on the horizon, promising dynamic control over light transmission and heat gain.
Impact of Smart Windows on Energy Consumption
Smart windows, equipped with electronic actuators, can adjust their transparency based on external conditions. This dynamic control can significantly reduce energy consumption by actively mitigating heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. For instance, a smart window could darken in the summer to prevent excessive solar heat gain, reducing the need for air conditioning.
Conversely, in the winter, the window could lighten to maximize solar heat gain, thereby minimizing the use of heating systems. The ability to dynamically regulate light transmission is a game-changer for energy efficiency, and the technology is rapidly progressing towards wider implementation.
Influence of New Materials and Designs on Energy Efficiency
New materials and designs are revolutionizing window construction. The development of highly efficient insulating glass units (IGUs) with multiple panes and specialized gas fills (like argon or krypton) enhances thermal insulation. These improvements lead to reduced heat transfer and minimized energy loss, making homes and buildings more comfortable while decreasing the reliance on HVAC systems. Advanced polymer films are also being incorporated into window designs, providing both excellent thermal insulation and UV protection.
The increased use of these advanced materials, coupled with sophisticated manufacturing processes, is enabling the creation of windows that perform better than ever before.
Predictions for Future Energy-Efficient Window Development
The future of energy-efficient windows will likely see a greater integration of smart technologies. These systems could be interconnected with building management systems (BMS), enabling automated adjustments to window settings based on real-time weather conditions and occupancy patterns. Furthermore, advancements in material science could lead to the creation of self-cleaning and self-healing windows, further enhancing their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
For example, self-cleaning windows could reduce the need for frequent cleaning, thus improving overall sustainability.
Comparison to Existing Solutions
Current energy-efficient windows, such as those utilizing low-e coatings and laminated glass, have significantly improved thermal performance over older models. Future trends will build upon these advancements by incorporating smart technologies and more advanced materials. The integration of smart window technology represents a significant leap forward, enabling dynamic control over energy usage. The combination of smart technology with traditional high-performance materials is likely to lead to windows that are significantly more efficient than current standards.
For example, a home equipped with smart windows can potentially reduce energy consumption by 15-20% compared to homes with traditional windows.
Comparison with Conventional Windows
Energy-efficient windows represent a significant advancement in building materials, offering substantial improvements over conventional windows. This difference translates directly into lower energy bills and a reduced environmental footprint. This section details the key performance distinctions and contrasts the two types of windows.
Performance Comparison
Conventional windows often have limited insulation capabilities, leading to significant heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This necessitates higher energy consumption for heating and cooling, impacting both the household budget and the environment. Energy-efficient windows, on the other hand, are engineered with advanced technologies to minimize these losses. They use multiple layers of insulated glass, low-E coatings, and advanced framing materials to effectively trap heat, resulting in substantial energy savings.
Key Differences in Energy Efficiency
The primary difference in energy efficiency lies in the materials and construction of the windows. Conventional windows typically consist of a single pane of glass with a simple frame. Energy-efficient windows incorporate multiple panes of insulated glass, often with low-emissivity (low-E) coatings. These coatings reflect heat back into the building, preventing unwanted heat transfer. Moreover, the frames of energy-efficient windows are often made of materials with superior insulation properties.
These factors contribute to a significantly reduced rate of heat loss and gain compared to conventional windows.
Comparative Table
| Feature | Energy-efficient Windows | Conventional Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Multiple panes of insulated glass with low-E coatings, and often thermally broken frames, leading to significantly lower heat transfer. | Single pane of glass with a simple frame, resulting in higher heat transfer and loss. |
| Cost | Generally higher upfront cost due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes. | Lower upfront cost due to simpler construction. |
| Lifespan | Typically have a longer lifespan due to the durability of the materials and advanced construction, lasting 20-30 years or more. | Typically have a shorter lifespan, potentially lasting 10-15 years, depending on the quality and environmental conditions. |
Cost Considerations
While energy-efficient windows have a higher initial cost, the long-term savings on energy bills make them a worthwhile investment. The reduced energy consumption translates to lower utility bills over the window’s lifespan. The higher initial investment is often offset by the savings over time. Factors like local energy prices and climate conditions play a role in determining the payback period.
Lifespan and Durability
The durability and longevity of energy-efficient windows often surpass those of conventional windows. The use of advanced materials, including multiple layers of insulated glass and reinforced frames, contributes to a longer lifespan. This translates to lower replacement costs and reduced environmental impact over the window’s lifetime. In contrast, conventional windows may require more frequent replacements due to deterioration.
Addressing Common Concerns
Energy-efficient windows, while offering significant benefits, often face misconceptions and concerns. Understanding these concerns, along with the pros and cons of various types, is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into common myths and realities, installation considerations, and cost factors to help you choose the best windows for your needs.
Common Misconceptions about Energy-Efficient Windows
Many people harbor misconceptions about energy-efficient windows, leading to hesitation in making the switch. These windows are often perceived as being more expensive or less aesthetically pleasing. However, advancements in technology have addressed these concerns. Modern energy-efficient windows are often comparable in appearance to traditional windows while significantly improving energy performance.
Pros and Cons of Different Energy-Efficient Window Types, Energy-efficient windows
Different types of energy-efficient windows offer varying levels of performance and features. Choosing the right type depends on your specific needs and budget. For example, double-paned windows are a popular and affordable choice, offering a good balance of performance and cost. Triple-paned windows, while more expensive, provide superior insulation and lower energy bills, especially in extreme climates.
Low-E coatings, which reflect heat, are commonly incorporated in various window types and improve energy efficiency.
Cost and Installation Issues
The initial cost of energy-efficient windows can be higher than traditional windows. However, this increased cost is often offset by long-term energy savings. The installation process can also be more complex for certain types of windows. Professional installation is essential to ensure proper sealing and maximize performance. Consider getting multiple quotes from reputable window installers to compare prices and understand the installation process.
It’s important to weigh the initial investment against potential long-term energy savings.
Choosing the Right Windows for Specific Needs
Selecting the appropriate energy-efficient windows depends on factors like climate, budget, and personal preferences. For example, in areas with harsh winters, triple-paned windows with low-E coatings might be the best choice. For those looking for a balance of performance and cost, double-paned windows with advanced glazing can be a suitable option. Consider your home’s architectural style and the overall aesthetic when making your decision.
Common Myths and Realities about Energy-Efficient Windows
Several myths surround energy-efficient windows. One common myth is that these windows compromise aesthetics. In reality, modern designs offer a wide range of styles and colors, making them a visually appealing choice. Another misconception is that they are overly expensive, though the long-term energy savings often outweigh the initial investment. A crucial reality is that proper installation is essential for maximizing performance.
Last Recap
In conclusion, energy-efficient windows offer a compelling combination of financial savings, environmental benefits, and enhanced comfort. By understanding the different types, features, and installation procedures, homeowners can make informed decisions to optimize their homes’ energy efficiency. The future looks bright for even more advanced technologies and innovations in this area.
FAQ Explained
How much do energy-efficient windows cost?
The cost of energy-efficient windows varies significantly depending on the type of window, features, and the installer. Generally, they are more expensive upfront than standard windows, but the long-term savings on energy bills often outweigh the initial investment.
What are the different types of energy-efficient windows?
Common types include double-pane, triple-pane, and windows with low-E coatings. Each type offers varying levels of insulation and energy efficiency. Double-pane windows are a good starting point, while triple-pane and low-E coatings provide even better insulation and performance.
Are energy-efficient windows worth the cost?
Yes, energy-efficient windows are often a worthwhile investment. The reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling, coupled with potential tax credits or rebates, frequently makes them a good financial decision in the long run.
What’s the difference between low-E and standard glass?
Low-E glass has a special coating that reflects heat. This means less heat is transferred into or out of your home, resulting in better energy efficiency compared to standard glass. This leads to reduced heating and cooling costs.
- Soundproof Glass Your Guide to Quieter Spaces - February 16, 2026
- Energy-efficient windows Smarter Choices - February 15, 2026
- How to Calculate the Right Amount of Outdoor Lighting for My Property - February 8, 2026