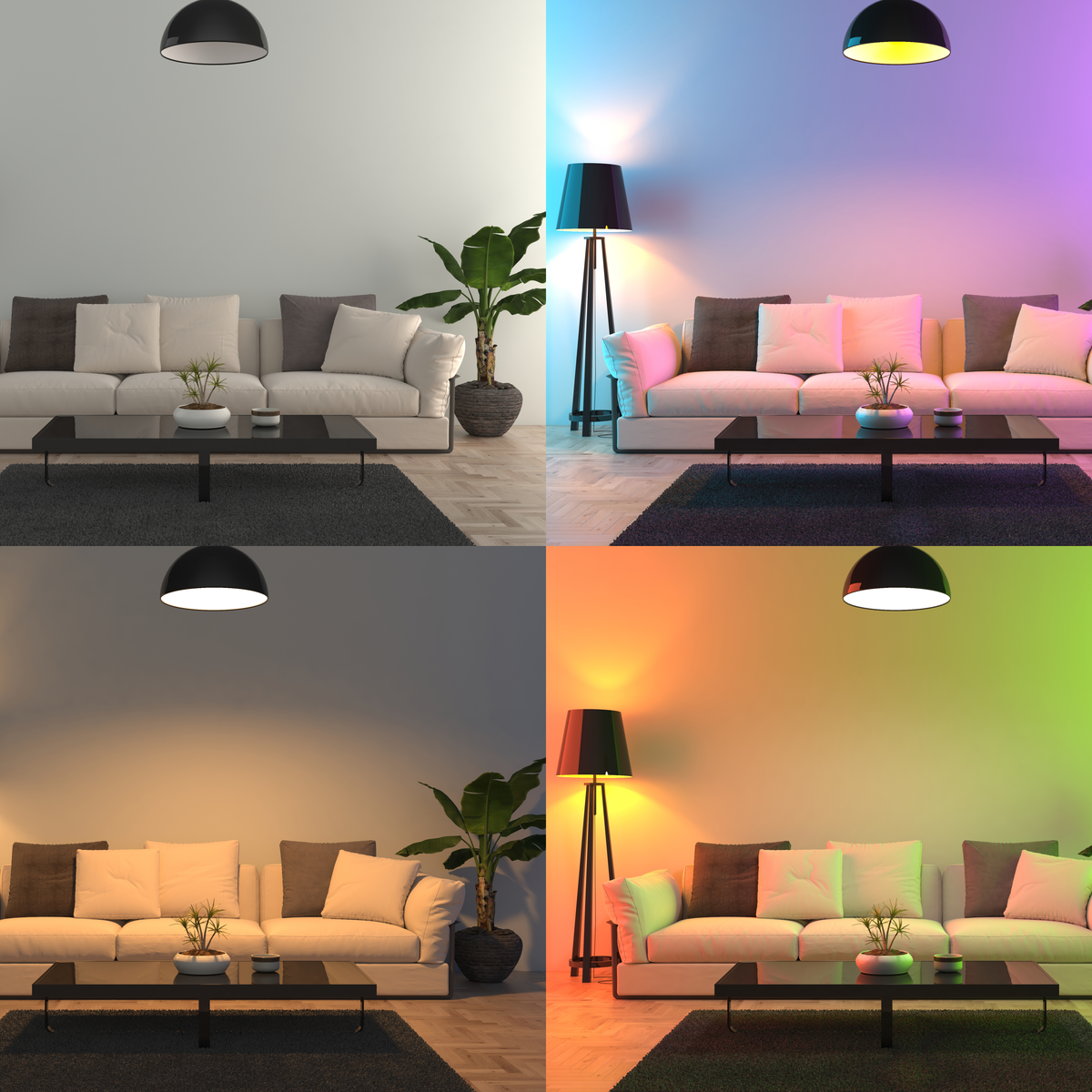
Smart lighting system is transforming how we illuminate our homes, offices, and public spaces. Imagine lights that adjust automatically to your needs, saving energy and creating the perfect ambiance. This system offers a multitude of benefits, from energy efficiency and cost savings to enhanced safety and security.
This overview explores the various aspects of smart lighting systems, including their components, technologies, applications, and future trends. We’ll also delve into the security considerations and compare them with traditional lighting systems.
Introduction to Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems are rapidly transforming how we interact with and control illumination in various settings. These systems leverage digital technology to automate, optimize, and personalize lighting experiences, leading to significant energy savings and enhanced comfort. They are becoming increasingly prevalent in homes, offices, and industrial spaces.Smart lighting systems go beyond simply turning lights on and off. They integrate with other smart home devices, allowing for seamless control and automation.
This integration opens doors for new possibilities in lighting design, energy efficiency, and even security.
Key Components of a Smart Lighting System
Smart lighting systems typically comprise several interconnected components. These components work together to deliver automated and responsive lighting solutions.
- Light Fixtures: These are the physical components housing the lighting technology. Modern fixtures often incorporate smart technology directly, or they can be equipped with smart modules or controllers.
- Control System: This is the “brain” of the system. It manages the communication between all components and receives instructions from users or external triggers. This often includes a central hub or gateway device.
- Sensors: These devices detect changes in the environment, such as presence, ambient light levels, or temperature. This data is used to adjust lighting settings automatically.
- Communication Protocol: This establishes how different parts of the system communicate. Examples include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Z-Wave, or others.
Smart Lighting Technologies
Different technologies power smart lighting systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of technology depends on factors like budget, complexity of the system, and desired functionality.
Smart lighting systems are becoming super popular, and for good reason. They’re perfect for a modern beach house like this one , allowing you to customize the ambiance for any occasion. From dramatic sunsets to cozy evenings, the flexibility of smart lighting is key.
- LED (Light Emitting Diodes): LEDs are the dominant technology in smart lighting due to their energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. They can be easily controlled digitally, enabling dynamic adjustments to light output and color temperature.
- DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface): DALI is a widely used protocol for professional lighting systems. It allows for sophisticated control of individual luminaires, particularly useful in commercial and industrial settings.
Control Methods in Smart Lighting Systems
Different control methods facilitate communication and interaction with smart lighting systems.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi offers a widespread and readily available connectivity option, making it popular for residential and smaller commercial settings. It often provides a seamless integration with existing home Wi-Fi networks.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology, often employed in applications where close proximity between devices is required. It is suitable for local control and can be more energy-efficient than Wi-Fi.
- Z-Wave: Z-Wave is a low-power, mesh networking technology. It’s particularly useful for larger installations where multiple devices need to communicate reliably and efficiently. Its low power consumption is beneficial for long-term operation.
Examples of Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems are increasingly implemented in various environments.
- Residential: Smart lighting systems in homes allow users to control lights remotely, schedule lighting for various times, and integrate with other smart home devices.
- Commercial: In offices, smart lighting can respond to occupancy levels, adjust brightness based on natural light, and enhance the work environment.
- Industrial: Smart lighting in factories or warehouses can optimize lighting for specific tasks, enhance safety, and minimize energy waste.
Comparison of Smart Lighting Technologies
| Technology | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| LED | Energy-efficient, long lifespan, customizable color temperature, compact size | Reduced energy bills, minimal maintenance, enhanced aesthetics |
| DALI | Digital control, precise dimming, individual luminaire control, advanced scheduling | Enhanced control and precision, suitable for complex lighting scenarios, optimized energy use |
Benefits and Advantages: Smart Lighting System
Source: thesmarthomejourney.com
Smart lighting systems offer a multitude of benefits, extending beyond simple illumination. These systems, by integrating technology and automation, enhance energy efficiency, reduce costs, and elevate safety and security. They also provide greater convenience and control, and can significantly improve the aesthetic appeal of any space.Smart lighting systems are designed to be adaptable and responsive, optimizing lighting based on real-time needs.
This adaptability results in substantial improvements in various areas, such as cost savings, environmental impact, and user experience.
Energy Efficiency Gains
Smart lighting systems achieve significant energy savings through advanced features like occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting, and automated dimming. These features detect when a space is unoccupied and automatically adjust or turn off lights, preventing unnecessary energy consumption. Daylight harvesting sensors further optimize energy use by dimming lights when sufficient natural light is available. This dynamic adjustment can result in substantial energy savings, potentially reducing electricity bills and lessening the environmental footprint.
For example, a commercial office building implementing smart lighting could see a 20-30% reduction in energy consumption dedicated to lighting, according to studies published by the US Department of Energy.
Cost Savings
Reduced energy consumption directly translates into lower electricity bills. Beyond direct savings, smart lighting systems can also lead to maintenance cost reductions. Automated systems minimize the need for manual adjustments, reducing labor costs. Furthermore, the extended lifespan of LEDs, often integrated into smart lighting systems, contributes to long-term cost savings by decreasing the frequency of bulb replacements.
The long-term cost savings from reduced energy bills and maintenance needs are significant for businesses and homeowners alike.
Improved Safety and Security
Smart lighting systems can significantly enhance safety and security. By strategically positioning and controlling lighting, these systems deter potential intruders and create a safer environment. Motion sensors and timed lighting schedules create an illuminated pathway or area, deterring potential threats and increasing visibility in areas that would otherwise be dark. This proactive approach to security can lead to reduced incidents of crime and accidents, resulting in a more secure environment.
Enhanced Convenience and Control Options
Smart lighting systems provide unprecedented levels of convenience and control. Users can remotely adjust lighting settings, schedule lighting routines, and control various lighting functions through mobile apps or voice commands. This ease of use allows for precise control of lighting, tailoring the ambiance of a space to specific needs or preferences. Users can instantly dim or brighten lights, change colors, or activate different lighting scenes, providing an unparalleled level of control and convenience.
Improved Ambiance and Aesthetics
Smart lighting systems offer a wide range of color options and adjustable brightness levels, enabling users to create a desired ambiance. Programmable lighting schedules can transform a space for different times of day or events, setting a specific mood or creating a particular aesthetic. The use of color-changing LEDs allows for the creation of dynamic lighting displays, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and providing a unique experience.
For example, a home theater room could be illuminated with various colors and patterns, enhancing the immersive experience.
Environmental Benefits of Smart Lighting
| Benefit | Details |
|---|---|
| Reduced Carbon Footprint | By decreasing energy consumption, smart lighting systems contribute to lower carbon emissions and a reduced environmental impact. |
| Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Reduced energy consumption translates to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. |
| Resource Conservation | The extended lifespan of LEDs in smart systems reduces the need for frequent bulb replacements, conserving resources. |
| Waste Reduction | Minimized bulb replacements translate to less waste generated from discarded light bulbs. |
| Promoting Sustainability | Smart lighting systems contribute to a more sustainable future by promoting energy efficiency and responsible resource management. |
Applications and Use Cases
Smart lighting systems are rapidly transforming various sectors, from homes to industries, by offering enhanced convenience, energy efficiency, and safety. Their adaptability allows them to be tailored to specific needs and environments, optimizing light output and control for optimal performance.Smart lighting systems are not just about replacing traditional bulbs; they are about revolutionizing how we use and manage light.
This adaptability is crucial, as different spaces require varying lighting levels, color temperatures, and scheduling needs.
Residential Applications
Smart lighting in residential settings offers homeowners a level of control and customization previously unimaginable. These systems can be programmed to adjust brightness and color temperature based on time of day, presence, or even user preference.
- Automated lighting schedules: Programmable timers and sensors can automatically turn lights on and off, based on the schedule of the residents or sunset/sunrise times, conserving energy and adding convenience. For instance, lights can turn off when the house is empty or turn on when someone enters a room.
- Presence detection: Motion sensors can detect when someone is in a room, adjusting lighting accordingly. This is useful in hallways, foyers, and even bedrooms. This feature adds safety and energy efficiency, as lights only illuminate when needed.
- Personalized lighting: Smart lighting systems can be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing users to adjust brightness, color, and even create customized scenes. This lets residents personalize the ambiance of their homes, for example, warm white light for relaxation, cool white light for focused work, or vibrant colors for a festive atmosphere.
Commercial Applications
Commercial spaces benefit from smart lighting’s ability to optimize energy consumption, enhance security, and improve employee productivity.
- Energy efficiency: Smart lighting can dynamically adjust brightness and color temperature based on occupancy and daylight availability, minimizing energy waste in offices and retail stores. This translates directly into cost savings for businesses.
- Improved security: Motion sensors and automated schedules can enhance security in commercial spaces, deterring unwanted activity and increasing safety for employees and customers. This is especially relevant for parking lots and exterior areas.
- Enhanced aesthetics: Customizable lighting schemes can transform the ambiance of retail stores and offices. This can create different moods or highlight specific products, increasing customer engagement and brand recognition. Color-changing lights can set the tone for events or promotions.
Industrial Applications
Smart lighting systems play a crucial role in industrial environments by enhancing safety, productivity, and operational efficiency.
- Improved visibility: Smart lighting systems can provide precise, adjustable illumination in warehouses and factories, minimizing accidents and improving operational efficiency. High-bay lighting can be controlled based on the activity occurring in a given area.
- Enhanced safety: Smart lighting systems can be integrated with other safety systems, such as emergency lighting and fire alarms, to ensure seamless operation during critical situations. This includes real-time monitoring of lighting conditions and automatic activation of backup lighting.
- Increased productivity: Optimized lighting can improve worker visibility and focus, potentially leading to increased productivity and reduced errors. Targeted lighting in manufacturing areas can improve the quality and precision of work.
Public Space Applications, Smart lighting system
Smart lighting systems can significantly enhance the aesthetics and safety of public spaces.
- Optimized street lighting: Smart streetlights can adjust brightness based on traffic density and pedestrian activity, saving energy while maintaining adequate visibility. This reduces unnecessary energy consumption and enhances safety for drivers and pedestrians.
- Enhanced safety and security: Smart lighting systems can be integrated with security cameras and other sensors to create a safer environment for citizens. This can include automated responses to suspicious activity.
- Improved aesthetics: Public spaces can benefit from dynamic lighting that changes color or brightness based on events or celebrations. This can enhance the atmosphere and create more engaging public areas.
Comparison of Use Cases Across Sectors
| Sector | Residential | Commercial | Industrial | Public |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduced energy consumption through presence detection and scheduling. | Significant energy savings through dynamic adjustments to lighting based on occupancy and daylight. | Optimized lighting for specific tasks and areas, reducing wasted energy. | Reduced energy consumption through automated adjustment of streetlights based on activity. |
| Security | Increased safety with automated lighting and motion detection. | Enhanced security with motion sensors and automated lighting schedules. | Improved safety and security with integrated lighting and alarm systems. | Increased safety and security through integrated lighting and monitoring systems. |
| Productivity/Aesthetics | Personalized lighting experiences for various moods and tasks. | Improved ambiance and customer engagement through customized lighting. | Enhanced visibility and productivity in manufacturing areas. | Improved aesthetics and ambiance in public spaces through dynamic lighting. |
Installation and Setup
Getting your smart lighting system up and running is easier than you might think. This section details the steps, tools, and considerations for a successful installation, from basic setups to integration with existing home automation. Follow these guidelines for a smooth and efficient installation process.
Step-by-Step Installation Procedure
This detailed procedure Artikels the installation process for a basic smart lighting system. It’s crucial to carefully follow these steps to ensure proper functionality and avoid potential issues.
- Preparation: Verify compatibility between your chosen smart bulbs/fixtures and your smart hub/controller. Ensure the necessary electrical connections are accessible. Gather all required tools and components.
- Installation of Smart Bulbs/Fixtures: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the smart bulbs/fixtures. This typically involves replacing existing bulbs with smart ones or connecting smart fixtures to existing electrical circuits. Pay close attention to polarity if applicable.
- Smart Hub/Controller Setup: Download the corresponding app on your smartphone or tablet. Follow the app’s instructions to add your smart lighting devices to the network. Ensure your smart hub/controller is connected to a reliable power source.
- Device Configuration: Configure the smart lighting devices within the app. Adjust settings like brightness, color temperature, and scheduling options to personalize your lighting experience.
- Testing and Verification: Test all the functions of the smart lighting system to confirm proper operation. Check the lighting’s responsiveness to commands and adjust settings as needed.
Necessary Tools and Equipment
A basic smart lighting system installation requires a few essential tools.
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Wire strippers/cutters
- Voltage tester
- Electrical tape
- Smart hub/controller (if required)
- Smart bulbs/fixtures
- Smartphone or tablet for app control
Connection Process for Different Devices
Different smart lighting devices have varying connection methods. The method depends on the type of fixture and smart bulb.
- Smart Bulbs: Smart bulbs typically replace existing incandescent or LED bulbs. The connection is straightforward, usually involving screwing the bulb into the fixture.
- Smart Fixtures: Smart fixtures require wiring, similar to traditional fixtures. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific wiring diagrams and procedures.
Troubleshooting Smart Lighting Systems
Common issues encountered during installation include connectivity problems, device misconfiguration, and incorrect wiring.
- Connectivity Problems: Check the Wi-Fi signal strength and ensure the smart hub/controller is within range. Restart the devices and the router to resolve connectivity issues.
- Device Misconfiguration: Double-check the device configuration within the app. Ensure the correct device is selected and the settings are correctly configured.
- Incorrect Wiring: Verify the wiring connections according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use a voltage tester to ensure the correct voltage is present at the fixture.
Integrating with Home Automation Systems
Integrating smart lighting with existing home automation systems, like smart home hubs, can enhance control and automation.
- Integration Process: Follow the integration instructions provided by the manufacturer of the home automation system and smart lighting devices. This often involves linking the accounts and configuring the devices within the home automation system.
- Example: A smart home hub could be programmed to automatically turn on the lights when a person enters a room or dim the lights based on the time of day.
Common Installation Errors and Solutions
Troubleshooting common installation errors can save time and effort.
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| Device not connecting to the network | Verify Wi-Fi connection, restart devices, and ensure the device is within range of the router. |
| Incorrect wiring | Recheck wiring diagrams and consult manufacturer’s instructions. Use a voltage tester to confirm correct connections. |
| Device not responding to commands | Restart the device, check app configuration, and update the app if available. |
Security and Privacy Considerations
Smart lighting systems, while offering convenience and energy savings, introduce new security and privacy concerns. Protecting these systems from unauthorized access and misuse, as well as safeguarding user data, is crucial for widespread adoption and trust. Robust security measures are essential to mitigate potential risks and ensure the responsible use of these systems.Implementing strong security protocols is vital for maintaining the integrity and reliability of smart lighting networks.
This involves not only protecting the physical infrastructure but also the data transmitted between devices and the cloud. Failure to address these concerns could lead to significant security breaches, compromising user privacy and potentially causing disruptions to the lighting system itself.
Security Measures in Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems often incorporate various security measures to protect against unauthorized access and manipulation. These include robust authentication protocols, encryption of data transmissions, and access control mechanisms. For example, many systems utilize multi-factor authentication, requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access. This adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized entry.
Smart lighting systems are becoming increasingly popular, and they’re a great way to enhance any home. A modern loft house, like the ones featured on Modern loft house , often incorporates these systems to create a sophisticated and stylish ambiance. The ability to adjust lighting levels and colors effortlessly makes them a key part of any smart home setup.
Potential Vulnerabilities of Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems, like any networked system, are susceptible to various vulnerabilities. These include weaknesses in the network infrastructure, flaws in the software controlling the lights, and vulnerabilities in the cloud services storing data. A compromised system could allow attackers to control the lights, potentially leading to outages, unwanted illumination patterns, or even data breaches. For instance, a security breach could expose user data like location information, activity patterns, or even financial details if integrated with other smart home systems.
Data Privacy Concerns Related to Smart Lighting Systems
Data privacy is a major concern with smart lighting systems. These systems collect and transmit significant amounts of data, including information about lighting usage patterns, occupancy, and even user activity within a home. Protecting this data from unauthorized access and misuse is paramount. Data encryption and anonymization are important techniques to minimize risks and safeguard user privacy.
Data retention policies should be transparent and user-controlled, allowing users to decide how their data is handled.
Measures to Enhance the Security of Smart Lighting Networks
Strengthening the security of smart lighting networks requires a multi-layered approach. Regular security updates and patching of vulnerabilities in the software are essential. Implementing strong network segmentation techniques, isolating different parts of the network, can limit the impact of a security breach. Using secure communication protocols, like HTTPS, for data transmission, can significantly improve security.
Best Practices for Securing Smart Lighting Installations
To secure smart lighting installations, adopting best practices is crucial. Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication should be enforced for all user accounts. Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Physical security measures, such as secure enclosures for network equipment, can also help protect against malicious tampering.
Comparison of Security Features Across Smart Lighting Brands
| Brand | Authentication | Data Encryption | Network Segmentation | Regular Updates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Multi-factor authentication, strong password policies | AES-256 encryption | Network segmentation, VLAN isolation | Regular security updates, automatic patching |
| Brand B | Two-factor authentication | TLS encryption | Limited network segmentation | Occasional security updates |
| Brand C | Basic password protection | No encryption | No network segmentation | No regular updates |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Specific security features may vary depending on the specific model and configuration of the smart lighting system. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for detailed information.
Future Trends and Innovations
Smart lighting systems are rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for energy efficiency and personalized experiences. This evolution promises exciting possibilities for how we interact with and benefit from lighting in our homes, workplaces, and public spaces. The future of smart lighting will be shaped by integrating cutting-edge technologies, leading to more sophisticated control, enhanced user experiences, and broader applications.
Emerging Technologies
Smart lighting systems are benefiting from a variety of emerging technologies, including advancements in LED technology, wireless communication protocols, and sensor technology. Improved LED chips offer higher efficiency and a wider range of color temperatures and intensities. These advancements enable more dynamic and nuanced lighting designs, offering more control over light output and quality. Wireless communication protocols, like Wi-Fi and Zigbee, facilitate easier integration and control of multiple lighting fixtures.
Sophisticated sensors, such as motion detectors and ambient light sensors, allow for more intelligent and responsive lighting adjustments.
Smart lighting systems are super useful for creating a modern vibe in your home. They can really enhance the clean aesthetic of a space, like the ones you’ll find in a Clean aesthetic house. Ultimately, a well-designed smart lighting setup can totally elevate the overall feel of any home.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are poised to significantly impact smart lighting systems. AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors to optimize lighting settings in real-time, adjusting brightness and color temperature based on factors like occupancy, time of day, and ambient light conditions. This optimization leads to significant energy savings, especially in commercial spaces. Furthermore, AI can personalize lighting experiences, creating dynamic and responsive environments that adapt to individual preferences and needs.
For instance, a smart home system might adjust the color temperature of lights to match the user’s mood or daily schedule.
New Control Methods and Interfaces
New control methods and interfaces are transforming the way we interact with smart lighting systems. Voice control, through systems like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, provides hands-free operation. Touchscreen interfaces and mobile apps offer intuitive and user-friendly control over lighting settings. These user-friendly interfaces enable users to personalize their lighting experiences, creating custom scenes and schedules, all from a convenient interface.
Furthermore, gesture recognition and other innovative interfaces are emerging, promising even more intuitive control and integration into everyday life.
Integration with Other IoT Devices
Smart lighting systems are increasingly integrating with other IoT devices. This integration creates a more connected and responsive smart home environment. For instance, a smart lighting system can automatically adjust its settings in response to information from other smart home devices, like thermostats, security systems, or smart appliances. This creates a more seamless and intelligent home automation experience.
Imagine a scenario where your lights automatically dim when the security system is activated.
Innovative Use Cases
Smart lighting is finding applications in a variety of innovative ways. In commercial spaces, smart lighting can dynamically adjust lighting levels to optimize energy consumption and create a more productive environment. In hospitals, it can be used to create therapeutic lighting settings to improve patient well-being. Retail stores are utilizing smart lighting to create immersive and engaging experiences for customers.
The applications are diverse and continue to expand as technology evolves.
Future Directions of Smart Lighting
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Energy Efficiency | Smart lighting systems will continue to optimize energy consumption by adjusting light output based on real-time data and user preferences. |
| Personalized Experiences | AI-powered systems will personalize lighting settings to match user preferences, moods, and activities. |
| Integration with Other IoT Devices | Integration with smart homes, security systems, and other devices will create more seamless and intelligent home automation. |
| Improved Control and Interfaces | Intuitive control methods, such as voice control and gesture recognition, will become more commonplace. |
| Expansion of Applications | Smart lighting will find new applications in diverse sectors, including healthcare, retail, and public spaces. |
Comparison with Traditional Lighting
Smart lighting systems offer a compelling alternative to traditional lighting, presenting significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental impact. Traditional lighting, while readily available and familiar, often falls short in these crucial areas. This comparison highlights the key differences and benefits of choosing smart lighting solutions.
Smart lighting systems are super useful, especially in a place like a coastal modern house. They can really enhance the ambiance of a space, like adjusting the lighting to match the changing weather outside, or automatically dimming lights based on the time of day. A great example of how smart lighting can be used to create a relaxing atmosphere is found in Coastal modern house designs.
These systems can really save energy too, which is a plus.
Energy Consumption
Smart lighting systems excel at energy efficiency. They leverage advanced control systems, such as occupancy sensors and daylight harvesting, to dynamically adjust light levels based on real-time conditions. This precise control minimizes wasted energy compared to traditional systems that operate on a fixed schedule. For example, a smart home using motion sensors to turn off lights in unoccupied rooms can save a substantial amount of energy compared to a house with lights left on continuously.
Smart lighting systems are becoming increasingly popular, especially for modern homes like Modern countryside home. They offer a fantastic way to control the ambiance and energy efficiency of your space. From automated schedules to personalized color palettes, smart lighting really elevates the home experience.
Furthermore, smart bulbs often use LED technology, which is inherently more energy-efficient than incandescent or halogen bulbs.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in smart lighting might seem higher than traditional options, the long-term cost savings often outweigh the upfront expense. Reduced energy consumption translates directly to lower electricity bills over time. Smart systems can also extend the lifespan of the lighting fixtures, minimizing the need for frequent replacements. For instance, a commercial building with a smart lighting system could see significant reductions in their energy bills, offsetting the initial cost of installation within a few years.
Maintenance Requirements
Traditional lighting systems often require more frequent maintenance, including bulb replacements and fixture repairs. Smart lighting systems, with their advanced control systems, reduce the need for manual adjustments and interventions. Predictive maintenance features in some systems can even alert users to potential problems before they become major issues, reducing downtime and minimizing costs associated with maintenance. This preventative approach is not readily available in traditional lighting systems.
Environmental Impact
Smart lighting’s reduced energy consumption directly translates to a lower carbon footprint. By minimizing energy use, smart systems contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions and a reduction in the overall environmental impact of lighting. Traditional lighting, particularly incandescent and halogen options, have a larger environmental impact due to their higher energy consumption and often use of non-renewable resources.
The shift towards smart, energy-efficient lighting is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future.
Summary Table
| Feature | Smart Lighting | Traditional Lighting |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Lower, dynamic adjustment based on real-time conditions | Higher, fixed schedules |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower long-term costs due to energy savings and extended lifespan | Higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements and energy consumption |
| Maintenance | Reduced maintenance requirements, predictive maintenance possible | Higher maintenance needs, frequent bulb replacements and repairs |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to energy efficiency | Higher carbon footprint due to energy consumption |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, smart lighting systems offer a compelling blend of convenience, energy efficiency, and enhanced security. From residential use to commercial and industrial applications, the possibilities are vast. While there are security considerations to address, the future of lighting is undeniably smart. This system is evolving rapidly, with new technologies and applications emerging constantly.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common installation errors for smart lighting systems, and how can they be solved?
Incorrect wiring, compatibility issues between devices, and faulty network connections are some common installation problems. Troubleshooting these often involves checking the wiring diagrams, ensuring device compatibility, and confirming a stable Wi-Fi or other network connection.
What are the key security measures for smart lighting systems?
Strong passwords, encryption, and regular software updates are vital. Also, using two-factor authentication and monitoring your system for unusual activity are recommended.
How does smart lighting compare to traditional lighting in terms of environmental impact?
Smart lighting systems, with their energy-efficient designs, generally have a lower environmental footprint. They can use less energy, leading to reduced carbon emissions and a smaller environmental impact.
What types of data privacy concerns are associated with smart lighting systems?
Privacy concerns often center around data collection and storage. Users should carefully review the privacy policies of the specific smart lighting system and consider opting for systems that prioritize data security.
- Privacy Glass Your Guide to Security & Style - February 16, 2026
- Folding Glass Wall A Versatile Design Solution - February 15, 2026
- Smart Lighting System Smarter Homes, Smarter Living - February 14, 2026









